Seed Reproduction * Description/Instructions ;The angiosperm ovule increases to mature seed size after fertilization, whereas in gymnosperms, this enlargement occurs prior to fertilization The general features of the reproduction of seed plants having now been summarized, certain special aspects of the reproduction in representative seed plants are described below Seed reproduction is when organisms reproduce by seeds This may include the combination of egg and sperm the reproductive pact of an organism

How Flowering Plants Reproduce Students Britannica Kids Homework Help
Seed production diagram
Seed production diagram-Among seed enterprises in the seed sector, for a more efficient delivery of a wider range of improved crop varieties and planting materials The final goal is to eventually develop a seed system which will be self sustaining, profitable and capable of delivering the Seed is the reproductive structure characteristic of all phanerogams The structure of seeds may be studied in such common types of pea, gram, bean almond or sunflower They are all built on the same plan although there may be differences' in the shape or size of the seed the relative proportion of various parts




Seed Dispersal For Kids Reproduction In Plants Youtube Seed Dispersal How To Memorize Things Seeds
Sexual reproduction involves pollen from one flower fertilising the egg of another to produce a seed Only one parent is needed in asexual reproduction and the offspring are exact copies Find outThe success of some invasive tree species is attributed, in part, to high fecundity in the form of sexual propagules If invasive trees produce more seed annually than cooccurring native trees, they will have a greater ability to disperse and establish across the landscape In this study, seed production of female Ailanthus trees was investigated to determine (1) reproductive age limits; Asexual Plant Reproduction May Seed New Approach for Agriculture Summary Farmers throughout the world spend an estimated $36 billion a year to buy seeds for crops, especially those with sought after traits such as hardiness and pestresistance
Reproduction seed plants Seeds produced by seed plants produced from the process of pollination (pollen fall on white) After that there will be a process of fertilization (conception), this process will evolve so that the resulting embryos will eventually be formed drupe Detailed descriptions please learn the material »Reproduction seed plants Rewiring plant reproduction for higher seed yields by University of Queensland Cowpea plant in flower Credit Brett Ferguson Exploiting quirks in plant reproductionSeed definition, the fertilized, matured ovule of a flowering plant, containing an embryo or rudimentary plant See more
Being pseudorandom instead of pure random means that, if you know the seed and the generator, you can predict (and reproduce) the output In this tutorial you will learn the meaning of setting a seed, what does setseed do in R, how does setseed work, how to set or unset a seed, and hence, how to make reproducible outputsPlant Reproduction Questions and Answers Get help with your Plant reproduction homework Access the answers to hundreds of Plant reproduction questions that are explained in"naked seed" Spores to reproduce _____ Common forest trees _____ "seed vessel" With needle shape PLANT REPRODUCTION HOW TO CLASSIFY HUGUET FITÉ, Janet CEIP Antoni Roig Lesson 2 Name _____ Activity 3 Botanists have developed a scientific




How Flowering Plants Reproduce Students Britannica Kids Homework Help




Seed Reproduction Pptx Powerpoint
Seed A seed is a part of a flowering plant involved in reproduction It consists of three major parts the embryo, endosperm, and testa The embryo is produced when male and female elements are combined during reproduction It will eventually grow into a new plantCan dormant seeds be stored longer than nondormant ones?Seed germination Some seeds germinate easily when spread on mineral wool under normal light, nutrition, moisture, and temperature conditions in the greenhouses Other seeds must be treated in order to promote their ability to germinate Temperature and moisture are usually decisive in determining whether a seed will germinate



How Seep Plants Reproduce Study Sheet Hanford Christian School Jane Kitson




Seed Dispersal Ck 12 Foundation
Seeds are also equipped to delay germination until growth conditions are optimal Pollen allows seed plants to reproduce in the absence of water The gametophytes of seed plants shrank, while the sporophytes became prominent structures and the diploid stage became the longest phase of the life cycle A seed is the egg cell of a plant, with a hard wrapper around it so it can survive on its own The earliest plants with seeds evolved from plants with spores during the late Devonian period, about 360 million years ago The seeds made a hard wrapper around the plant's reproductive cell, to protect it so that the new baby plant could surviveWell, it turns out the bananas do have seeds (of a sort) but they aren't used for reproduction




Ch 30 The Evolution Of Seed Plants Ch 38 Angiosperm Reproduction And Biotechnology Ch 39 Plant Responses To Inte In 21 Plant Physiology Biology Units Ap Biology




Effect Of Pcap2 On Arabidopsis Seed Germination Seedling And Download Scientific Diagram
Mast seeding, the intermittent, synchronous production of large seed crops by a population of plants, is a wellknown example of resource pulses that create lagged responses in successive trophic levels of ecological communities These lags arise because seed predators are thought capable of increasing reproduction and population size only after the resource pulse is Sexual reproduction requires genetic material (DNA) from two parents The parent plants have male and female sex cells, called gametes The genetic material from the male and female gametes combines to produce offspring This process is called fertilizationThe video explains how plants reproduce through seeds It shows how seeds germinate and what are required for germination It also explains the importance of
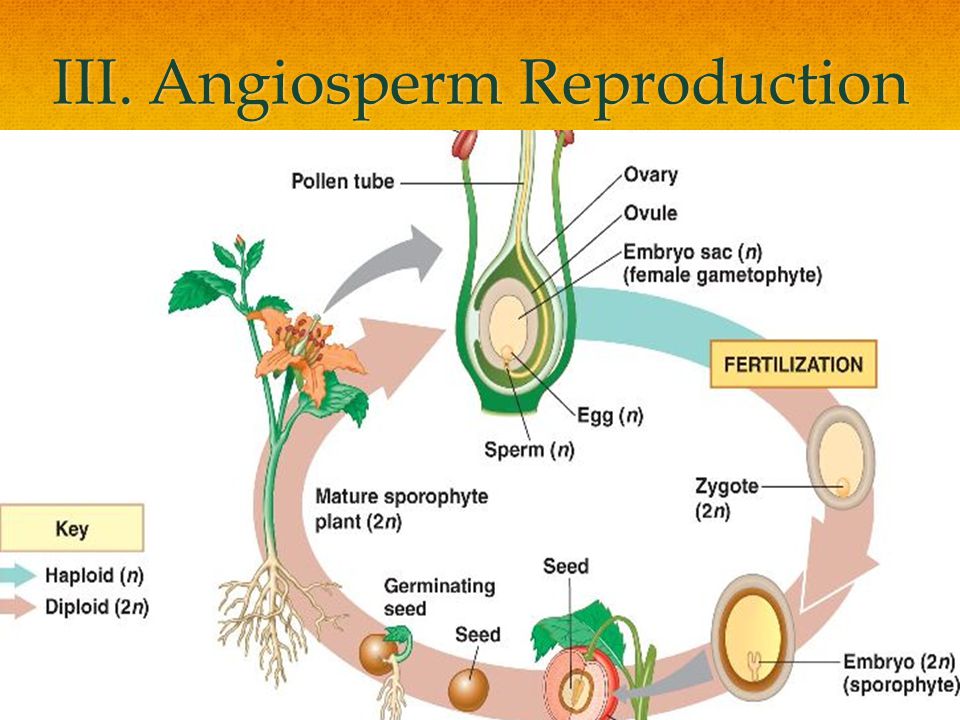



Chapter 7 Lesson 3 Seed Reproduction Ppt Video Online Download




Class 5th Science Reproduction In Plants Chapter 1 Youtube
Some growers keep the light female hermaphrodite plants to collect the pollen This pollen is the male part of the reproduction, but is nonetheless genetically female and produces seeds that produce virtually 100% female plants One way is by being exceptionally good at asexual reproduction One of the oldest living organisms on Earth is a peat moss in Hawaii that has been asexually reproducing since a single spore landed on the islands 50,000 years ago The other option, of course, is to reproduceThe adult sporophyte (eg pine tree) develops male and female cones on separate branches Female cone develops two ovules on the upper surface of each cone



Seed Plant Reproduction A Fourth Grade Smartboard Introduction By Mike Hyman



Growing Plant Stages Color Line Icon The Seed Germination Growth Reproduction Pollination And Seed Spreading Pictogram For Web Page Mobile App Promo Editable Stroke Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock
Modes Of Reproduction in Plants There are several ways by which plants produce their offspring These are categorised into two types (i) asexual, and (ii) sexual In asexual reproduction plants can give rise to new plants without seeds, whereas in sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from seedsFennel seeds have a high calcium content, and they are a source of iron, fibre, potassium, and magnesium They are edible and can be included as condiments in different dishes or can also be added to bread 9 Papaya seeds These type of seeds are entirely edible, and they can be eaten whole, ground or with some waterSection 3 Seed Reproduction small structure produced by the male reproductive organs of a seed plant;has a waterresistant coat, can develop from a spore, and contains gametophyte parts that will produce sperm transfer of pollen grains to the female part of the of a seed plant by agents such as gravity, water, wind, and animals




Seed Dispersal For Kids Reproduction In Plants Youtube Seed Dispersal How To Memorize Things Seeds
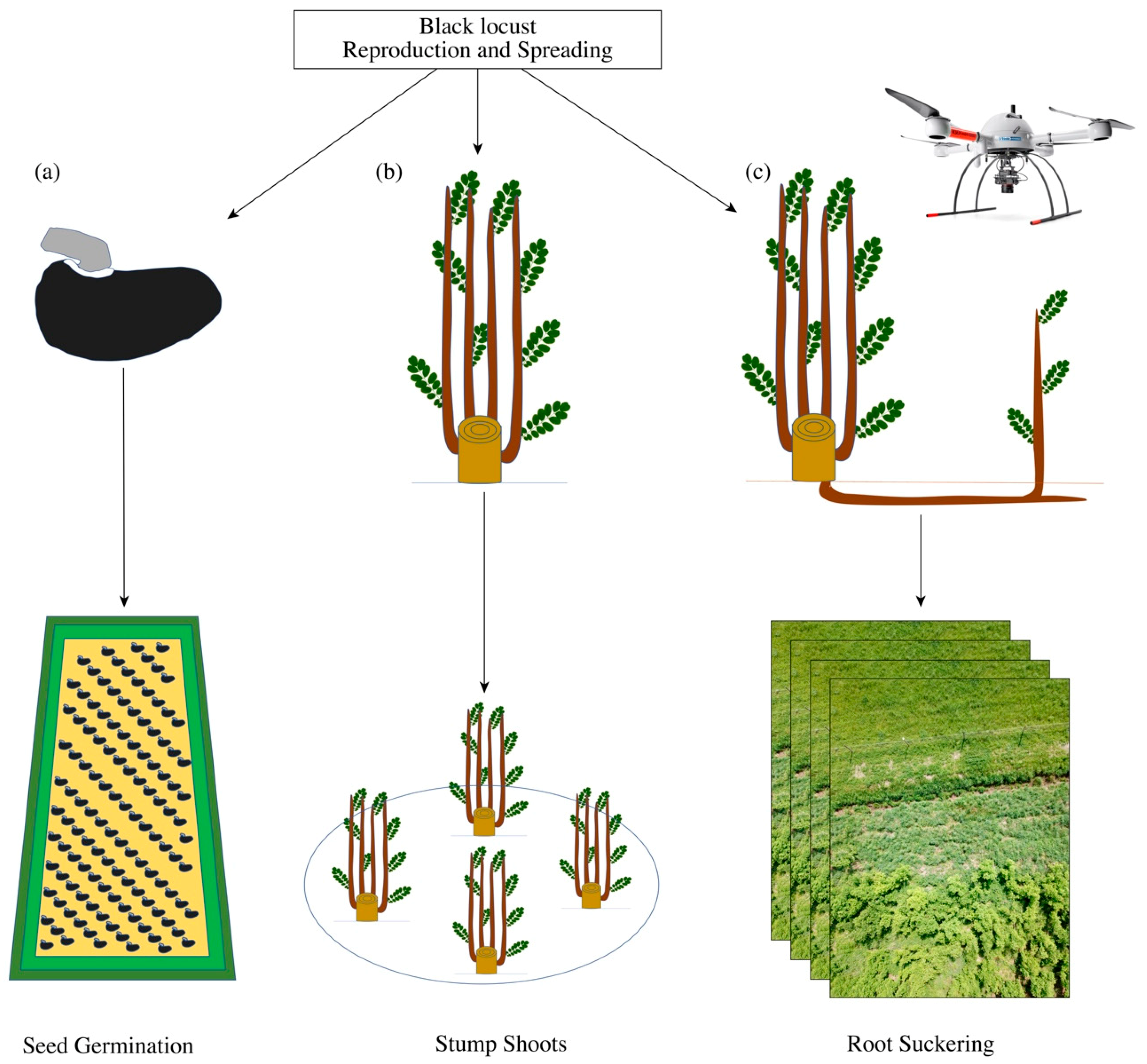



Forests Free Full Text Robinia Pseudoacacia L In Short Rotation Coppice Seed And Stump Shoot Reproduction As Well As Uas Based Spreading Analysis
Strawberry plants can reproduce through sexual reproduction with fruit and seed, as well as through asexual reproduction by sending out runners to create new plants, according to Garden Guides Runners, also called stolons, are sent out from the crown of a strawberry plant along the ground Nodes begin to appear on each stolon at set intervalsHemp Breeding and Seed Production is an 3 halfday online course designed to enhance the knowledge of professionals working on hemp improvement and propagation The course covers hemp seed production topics such as flowering, pollination, seedBut Sometimes no, for a seedlot that contains rotting pieces of fruit will probably go mouldy and the seeds die (See B 30–34 for more information on seed handling)




Plant Reproduction Sexual And Asexual Vegatitive Propogation Flashcards Quizlet



1
This quiz will discuss how seeds reproduce and what is needed in order for reproduction to happen Group Science Science QuizzesSeed Artillery works on many different types of projects and can often deliver results when others cannot The scope of the work done is very wide and is unique to the artillery piece that needs to be restored or repaired We meet NSSA standards on all replica work and hold each project to the highest standardsStage when reproduction takes place Pollination activities engage students actively in spreading pollen among plants so that they successfully reproduce and develop seed in the next stage In addition, this stage opens up the opportunity for linking students' use of bee sticks with explorations into the interactions of plants and insects



Www Cambriansd Org Cms Lib Ca Centricity Domain 390 Ppt as flower reproduction Pdf




Seeds And Flowers Plant Reproduction Plants Without Seeds
Annually variable and synchronous seed production by plant populations, or masting, is a widespread reproductive strategy in longlived plants Masting is thought to be selectively beneficial because interannual variability and synchrony increase the fitness of plants through economies of scale that decrease the cost of reproduction per surviving offspringSeed production of perennials may be unimportant relative to vegetative reproduction, but it should not be neglected In April 1990, one field bindweed seed was planted in a small planter, and on April 25, the twoleaf seedling was transplanted to a 2 × 4 × 16–ft box If you're the type to wonder about such things, you may have noticed that the bananas you buy at the store seem to contain no seeds If that's the case, how does the banana tree reproduce?




43 Chapter Plant Reproduction 43 4 How Do



1
A seed is a structure that encloses the embryo of a plant in a protective outer covering Under favorable conditions of growth, a seed gives rise to a new plant, using the nutrients stored in them The union of the male and female reproductive cells inside the ripened ovule of a flower helps in the formationSometimes yes for example a seedlot with hard seed coats will usually keep best if they have not yet been pretreated;The seed habit is the most complex and evolutionary successful method of sexual reproduction found in vascular plants Today, seed plants, gymnosperms ("Nacktsamer", ca 800 living species) and angiosperms ("Bedecktsamer", flowering plants, ca living species), are by far the most diverse lineage within the vascular plants (see figure below)



Ginseng Reproduction



Reproduction Mucuna Pruriens Velvet Bean Tropical Plant Used To Help Treat Parkinson S Disease
The evolution of seeds allowed plants to decrease their dependency upon water for reproduction Seeds contain an embryo that can remain dormant until conditions are favorable when it grows into a diploid sporophyte Seeds are transported by the wind, water, or by animals to encourage reproduction and reduce competition with the parent plant Key Terms GERMINATION PROCESS A seed with a tiny embryo inside remains in the ground until conditions are right for the seed to germinate After the seed coat splits the embryo root begins to grow into the soil Now the embryo can get water Food in the seed feeds the embryo as the shoot (stem) grows upward the lightTo make a seed a flower must be pollinated Pollen from the male part of one flower travels to the female part of another flower where the seeds are made Most, but not all plants, have both male




Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S




Rewiring Plant Reproduction For Higher Seed Yields
Seed production requires favorable weather conditions during flowering and the development of seeds, as well as the absence of damaging insects Pioneers, in general, produce more and lighter seeds Only the oaks (Quercus spp) do not follow this rule Storage conditions become important immediately after ripening of the seeds 1 Plant Reproduction 2 Reproduction of plants Plants Non Flowering flowering By Flowers & Vegetative Spores Cones Seeds reproduction formation 3 Plant Asexual Reproduction Above ground Stems arch over and take root at the tips, forming new plants (Forsythia, Raspberry and Strawberry) Horizontal above ground stems are called stolons 4Seed, the characteristic reproductive body of both angiosperms (flowering plants) and gymnosperms (eg, conifers, cycads, and ginkgos) Essentially, a seed consists of a miniature undeveloped plant (the embryo), which, alone or in the company of stored food for its early development after germination , is surrounded by a protective coat (the testa)




Reproduction Of Flowering Plants Zainab Waheed
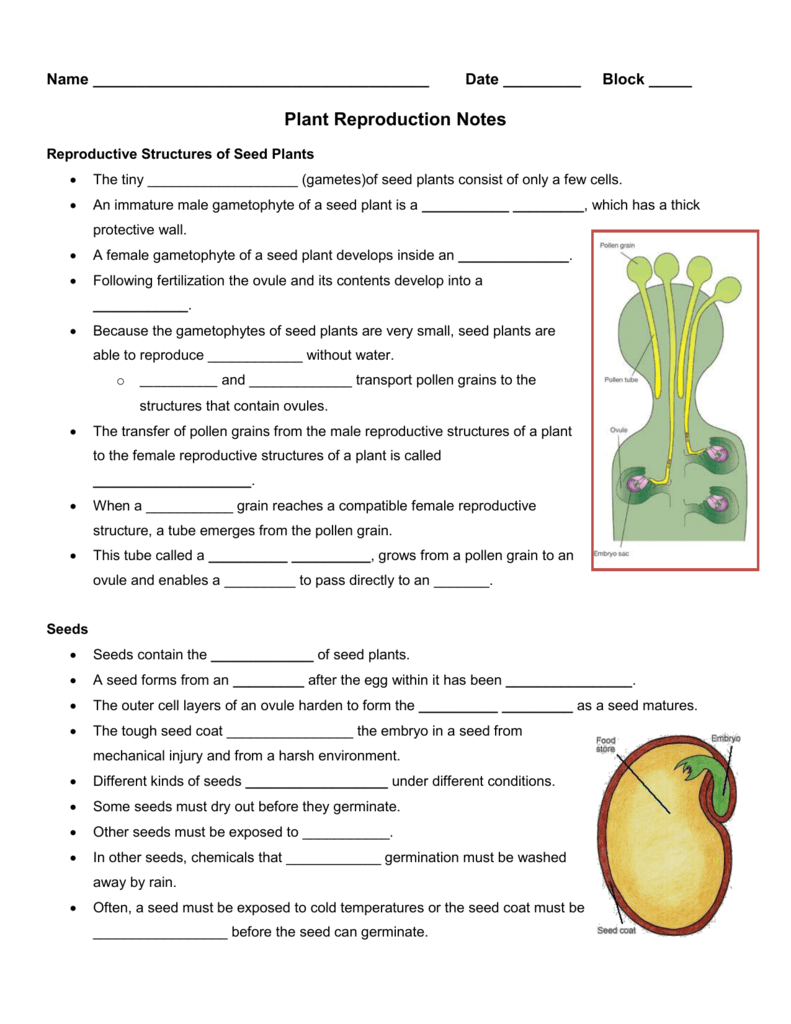



Plant Reproduction Notes Outline
Dandelion Reproduction The dandelion has more than one method of reproducing themselves This gives them multiple ways to spread and makes them more difficult to eradicate The most common method of dandelion reproduction is through its windaided dispersal of seeds which germinate almost yearround Pollination of the dandelion occurs when




5 Reproduction Of Plants How Do Plants Reproduce




Reach For The Sun Lesson 3 Plant Life Cycles And Reproduction Filament Games




Botany Plant Reproduction Laboratory Seed Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
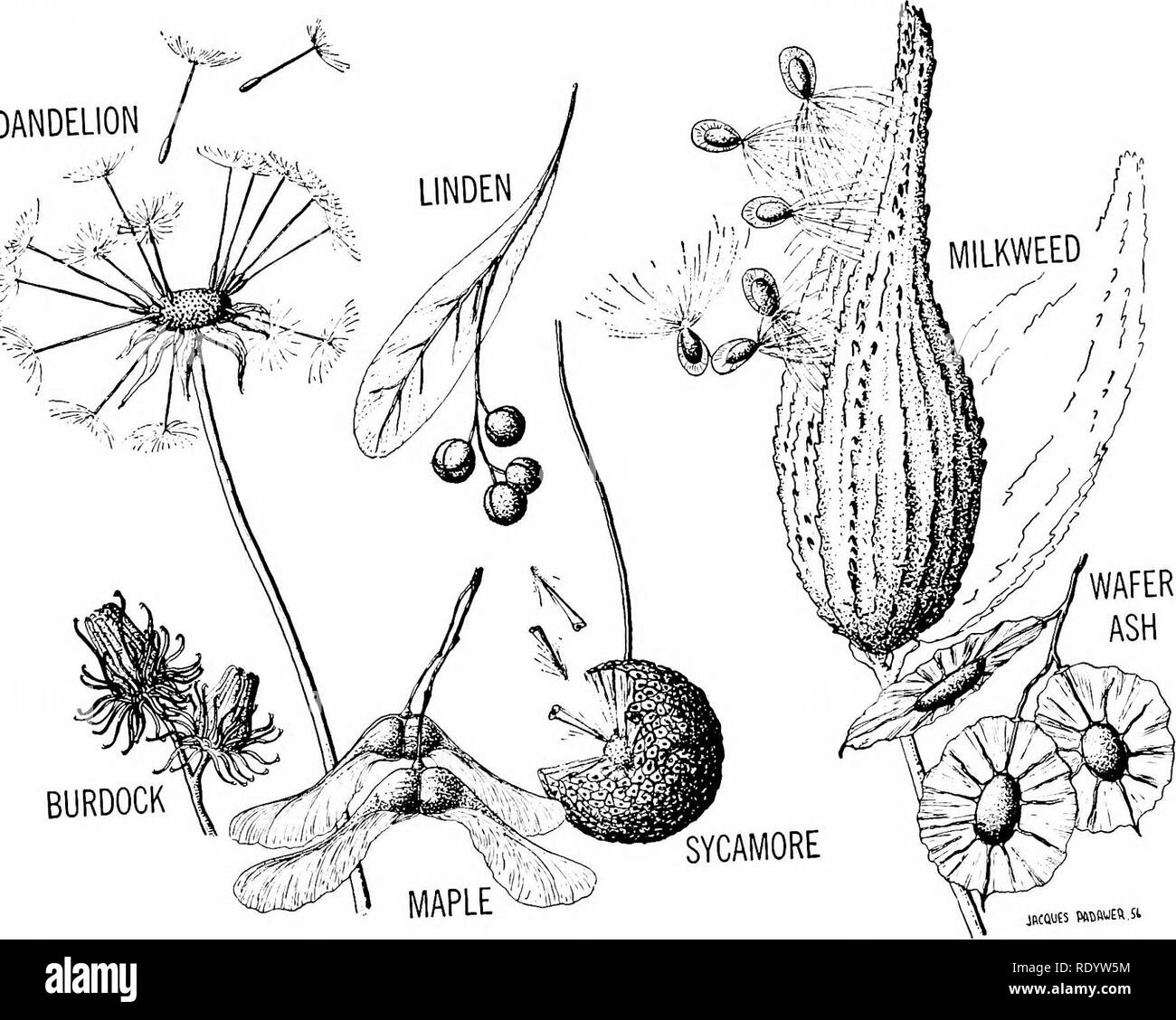



Principles Of Modern Biology Biology Reproduction In Multicellular Plants 229 Dandelion Jacques Ptowjeft Si Fig 12 31 Above Types Of Seed And Fruit Dispersal Mech Anisms Fig 12 32 Righ Some Common Berries Please Note



Plant Reproduction Seed Plants




Pin On Fruit Seeds



Plant Reproduction Drawing High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



Growing Plant Stages Black Glyph Icon The Seed Germination Growth Reproduction Pollination And Seed Spreading Pictogram For Stock Illustration Illustration Of Ground Concept



Plant Reproduction Drawing High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Plant Reproduction




Science Plant Reproduction Seed Dispersal Germination English Youtube




Where In The Venn Diagram Would Play The Term Seed Seed When Describing Plant Reproduction Brainly Com




Complex Body Seed Reproduction Flowering Angiosperms Plants Stock Photo Image By C Enigma Art




Pdf Sexual And Apomictic Seed Reproduction In Aronia Species With Different Ploidy Levels Semantic Scholar



Flowering Plant Reproduction




Sexual Reproduction In Plants The Seed The Seed Is The Product Of Sexual Reproduction In Most Plants The Seed Contains An Embryo A Food Supply Ppt Download




Ppt Chapter 24 Reproduction Of Seed Plants Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
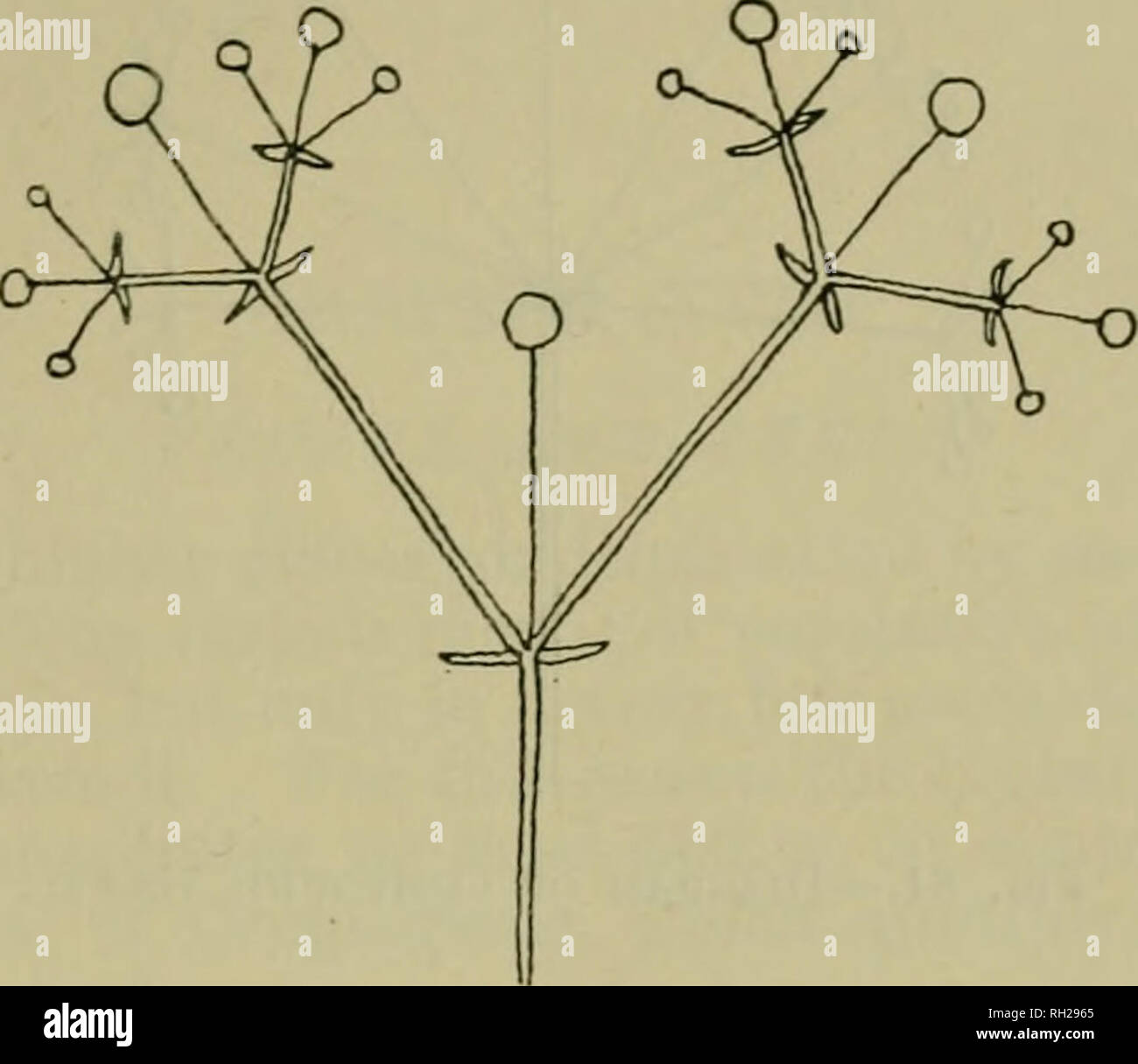



British Plants Their Biology And Ecology Plants Plant Ecology Reproduction By Seed 181 The Head Fig 80 Is The Characteristic Inflorescence Of The Dandelion Family The Scabious Thrift Etc The
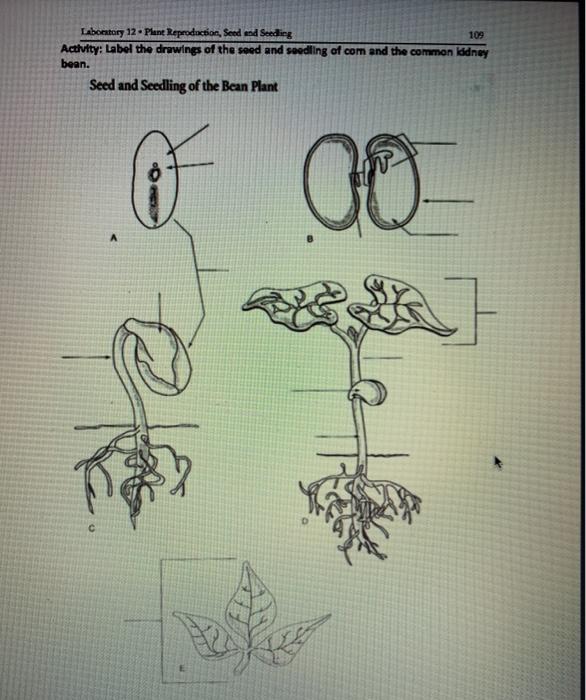



Laboratory 12 Plant Reproduction Seed End Seeding Chegg Com
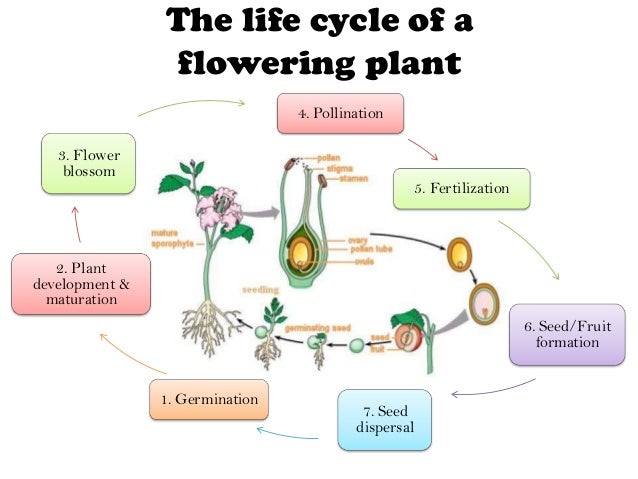



Pmr Form 3 Science Chapter 4 Plant Reproduction




Plant Reproduction System Fertilisation Pollination And Seed Germination Diagram Quizlet
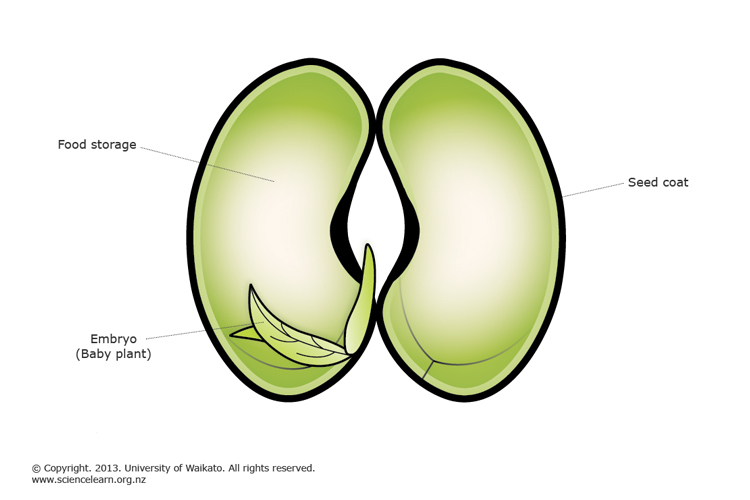



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




Amazon Com Vintage Art Print Wall Decor Floral Seed Pack Catalog Cover Art 8 X 10 Reproduction Unframed Posters Prints




Seed Reproduction By Fernanda J Fuentes




Plant Reproduction Seed Plants




Vegetative And Seed Reproduction Of Plants Tubers Bulbs And Seeds Isolated On White Background Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock



Tomatosphere Tomatosphere The Life Cycle Of A Tomato Plant




Vegetative And Seed Reproduction Of Vegetable Plants Potato Onion Garlic Stock Vector Illustration Of Generative Potato



How Do Trees Reproduce Quora




How Do Seed Plants Grow Reproduce



1



Reproduction In Flowering Plants Presentation Biology




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica




9 4 Reproduction In Plants Sl Hl 1 Biology 7 Ferguson




Complex Body Seed Reproduction Flowering Angiosperms Plants Stock Photo Image By C Enigma Art




Plant Reproduction Bioninja



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C



9 3 Reproduction In Angiospermophytes Bioninja




Plant Reproduction Wordsearch




Fern Reproduction Seed Less Vascular Plants Diagram Quizlet




Ovary Botany Definition Structure Britannica




Overview Of Sexual And Asexual Seed Development In Citrus Major Download Scientific Diagram




How Are Seeds Formed Animated Pollination And Fertilization Tutorial Botany Youtube




Learn Characteristics Of Living Organisms Nutrition Growth Reproduction And Lifespan In 3 Minutes




Reproduction Without Seeds By Hanisha Brar




Seed Reproduction Chapter 7 Section Ppt Download




Ch 24 Reproduction Of Seed Plants I Reproduction
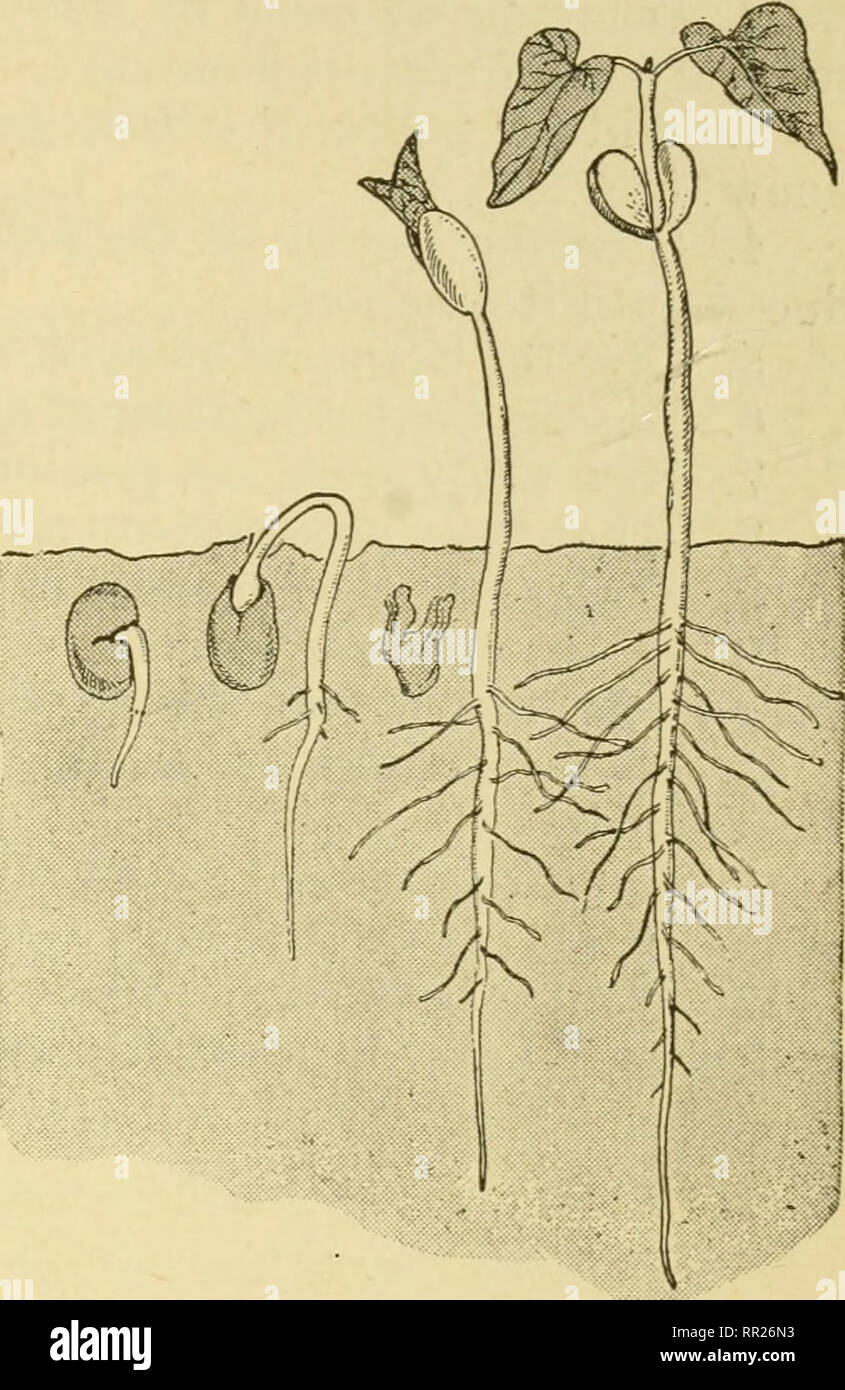



Advanced Biology Biology Physiology Reproduction Formation Of The Seed And Fruit 279 In The Grains The Endosperm Is A Well Developed Localized And Easily Identified Structure In Seeds Such As Beans Peas
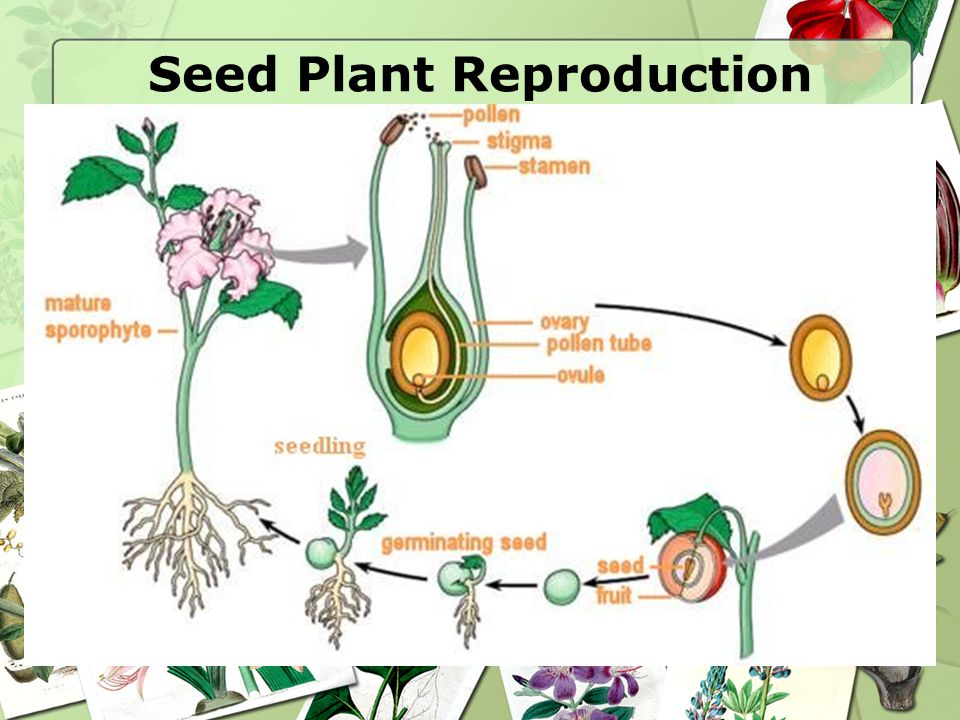



3 2 Notes Plant Reproduction Ppt Download




Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




Ppt Seed Plant Reproduction Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Plant Reproduction Seeds And Spores Cut And Paste Activity By King Virtue




Seed Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
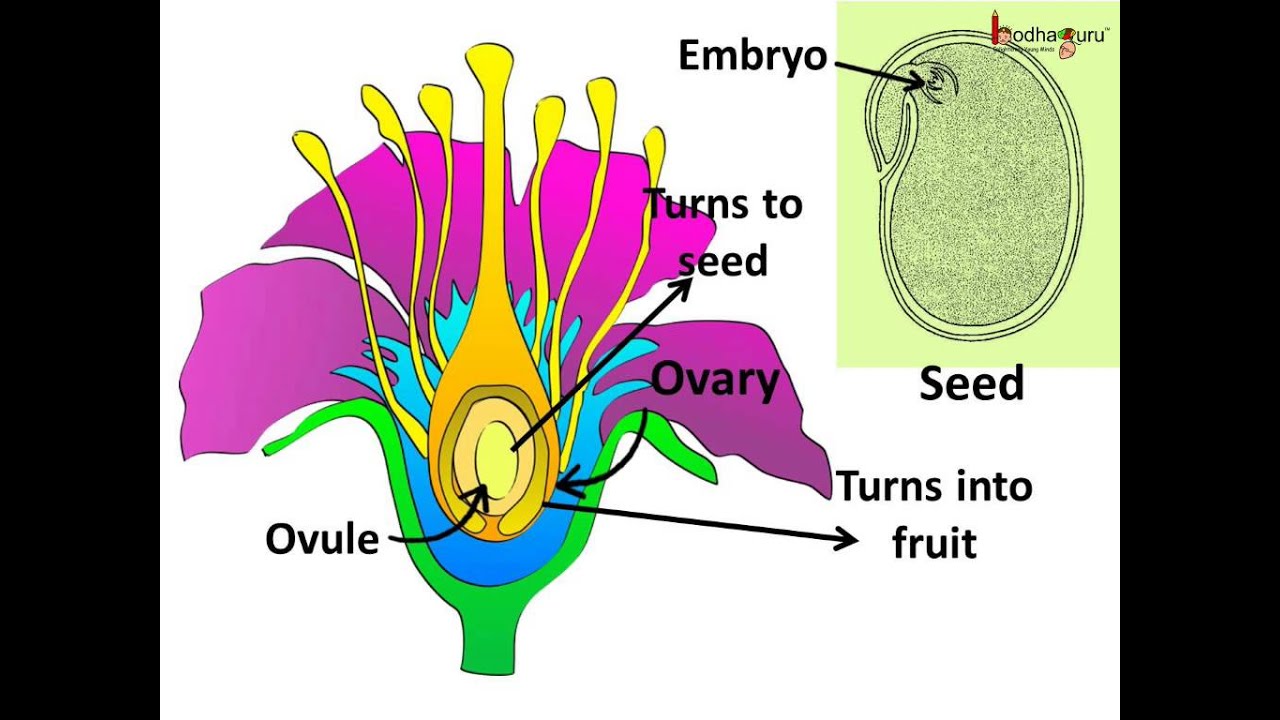



Science Sexual Reproduction In Plants Pollination Fertilization Hindi Youtube



Daffodil Reproduction




Fun Germination Facts For Kids
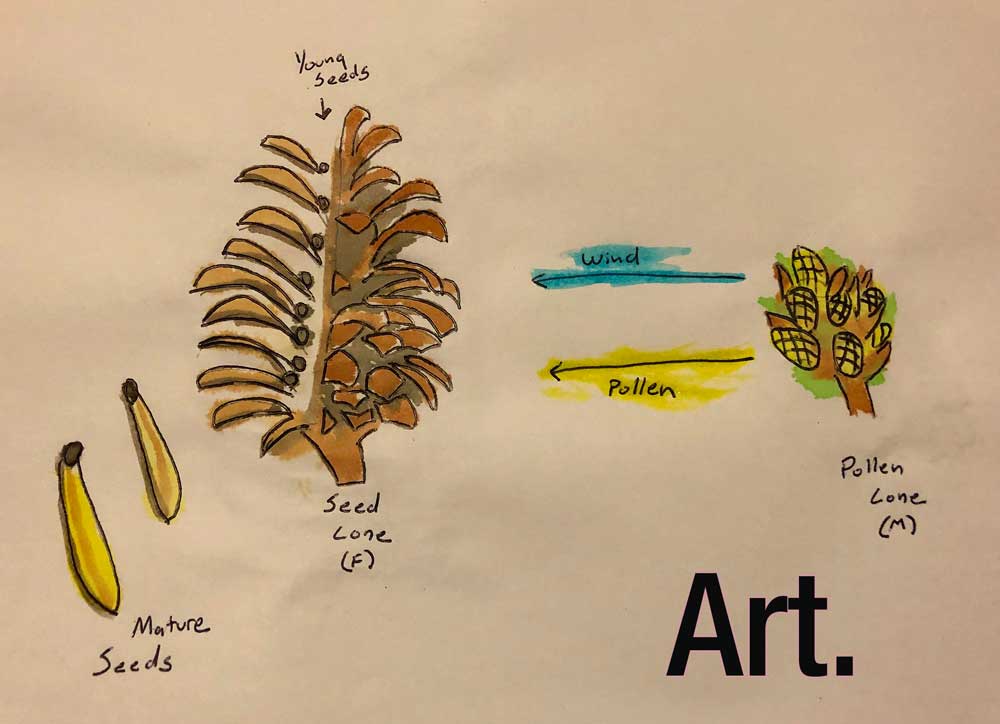



Outdoor Education School Science Camps California




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C




Reproduction System Reproduction Systems In Plants Seed Propagated
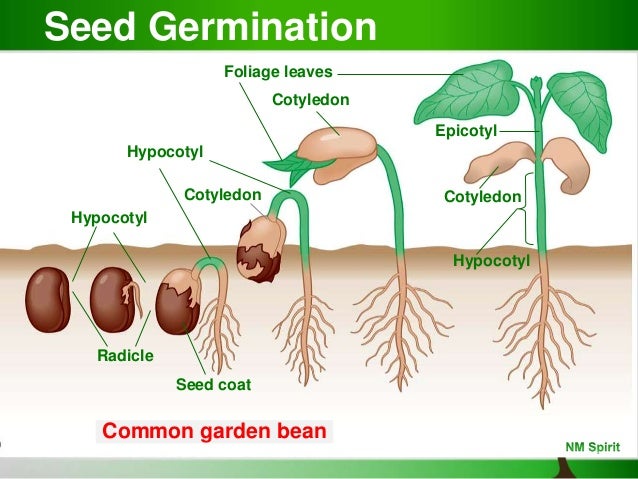



Plant Reproduction Development
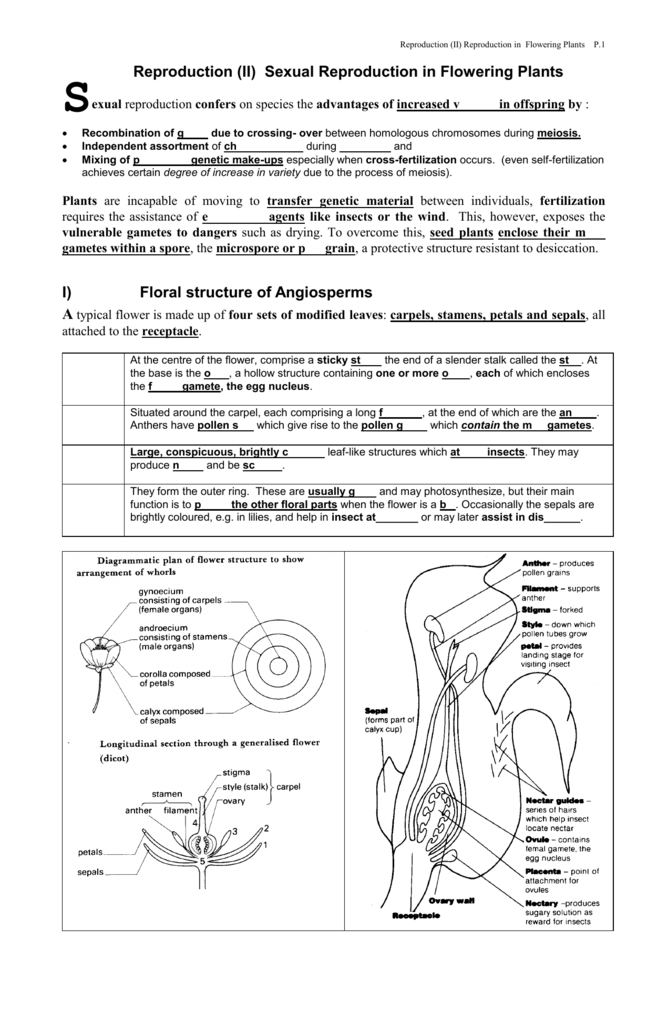



V Advantages And Disadvantages Of Reproduction By Seed
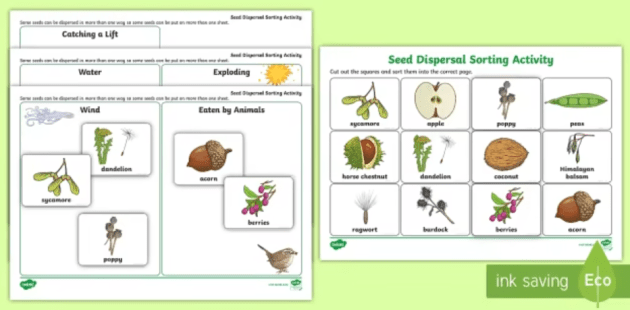



What Is Reproduction In Plants Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki



Plant Reproduction Biology Junction



B2 Sexual Reproduction In Plants Lydia G Narain




Complex Body Of Seed Reproduction Of Flowering Angiosperms Stock Photo Picture And Royalty Free Image Image
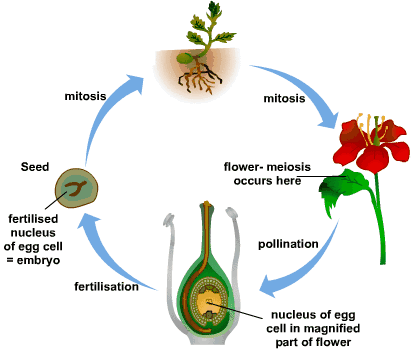



Mcq On Plant Reproduction By Biology Experts Notes Medium




Flower Reproduction Illustration Labeled Process Of New Plants Scheme Educational Diagram With Stamen And Pistil Structure And Full Egg Development And Fertilization Stages From Ovule To Seed Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And




Seed Dispersal Interactive Worksheet




Fun Germination Facts For Kids



1



The Seed Biology Place Seed Evolution




Plant Reproduction Seed Plants




Plant Reproductive System High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
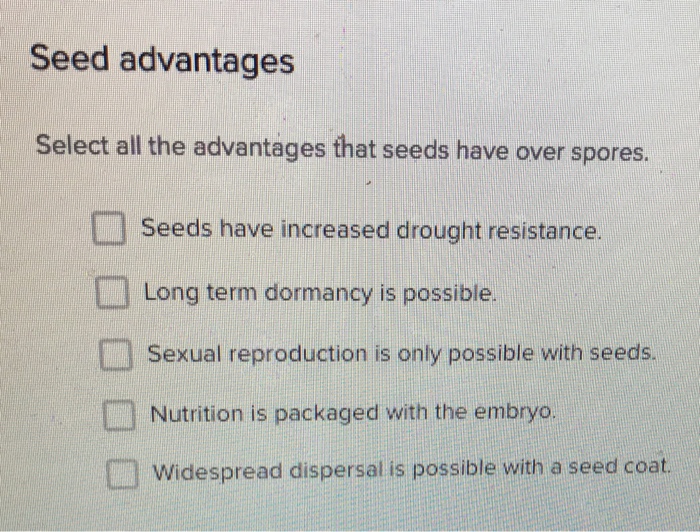



Select All The Advantages That Seeds Have Over Chegg Com




Jove Science Education Plant Reproduction
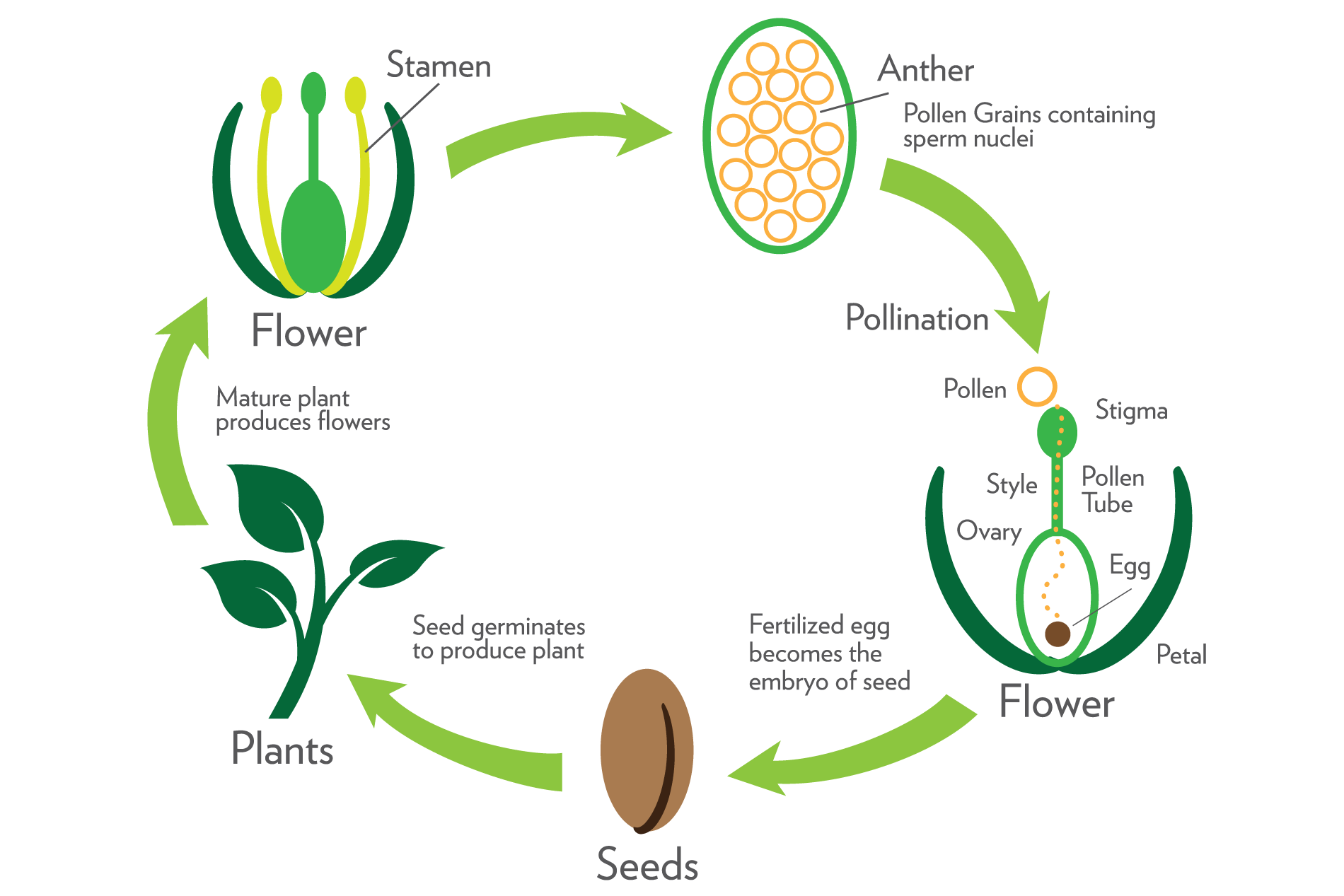



Part 3 Growth Reproduction And Evolution Plant Reproduction Dōterra Essential Oils
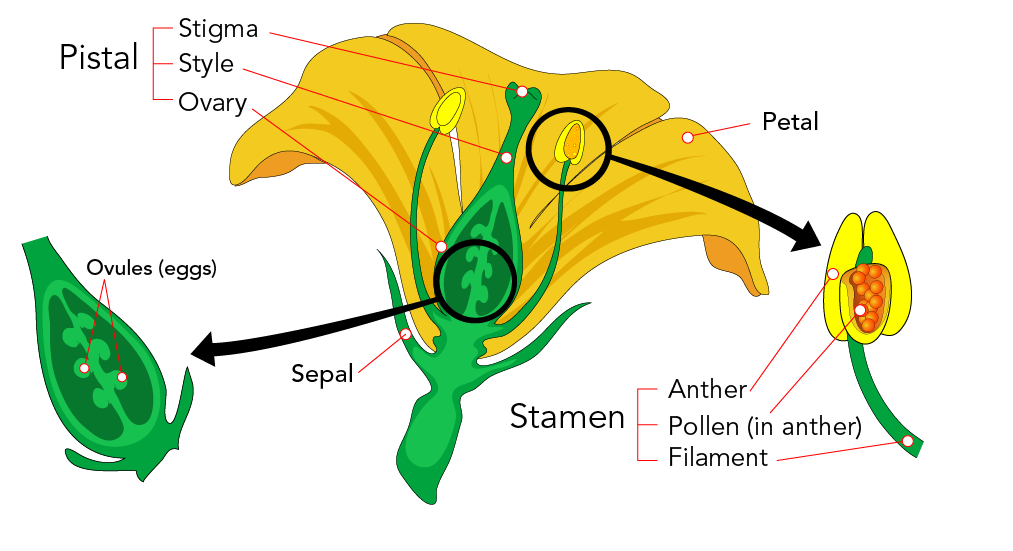



Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Spreading The Seeds Mini Poster Seed Dispersal Plant Reproduction Ngss




Seed Plants Classification Seeds Seedless Plants Mosses Ferns Ferns Are Vascular Plants Make Spores Not Seeds Embryo From Sexual Reproduction Ppt Download



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿